Professional Trading Account vs. Retail Trading Accounts

The distinction between professional and retail clients is rooted in the EU’s Markets in Financial Instruments Directive (MiFID), which has been incorporated into UK law. Retail clients are considered to have less experience, knowledge, and resources to manage the risks of trading, and thus they are afforded the highest level of regulatory protection. Professional clients, on the other hand, are deemed to have sufficient experience, knowledge, and resources to make their own investment decisions and properly assess the risks that they incur.
What Does This Mean?
In the UK, the distinction between retail and professional clients is a crucial aspect of the regulatory framework overseen by the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA). This differentiation is not merely a bureaucratic classification but a reflection of the FCA’s commitment to ensuring that investors are provided with a level of protection and access to financial products that corresponds to their experience, knowledge, and financial strength. Understanding this distinction is essential for anyone engaged in CFD trading and spread betting, as it impacts the range of products available to them, the level of protection they receive, and the strategies they may employ.
Retail Clients
Retail clients are typically individual investors who do not possess the same level of market knowledge, experience, or financial resources as professional clients. The FCA affords a higher level of protection to retail clients due to their presumed vulnerability. These protections include access to the Financial Ombudsman Service for dispute resolution, eligibility for compensation under the Financial Services Compensation Scheme (FSCS), and enhanced disclosure requirements from firms offering financial products.
Moreover, retail clients benefit from restrictions designed to minimize their risk exposure. For example, leverage limits for CFDs and spread betting are significantly lower for retail clients than for professional clients. This means retail clients can only access products with lower leverage, reducing potential losses (and gains). Additionally, retail clients are protected by negative balance protection, ensuring they cannot lose more money than they have deposited in their trading account.
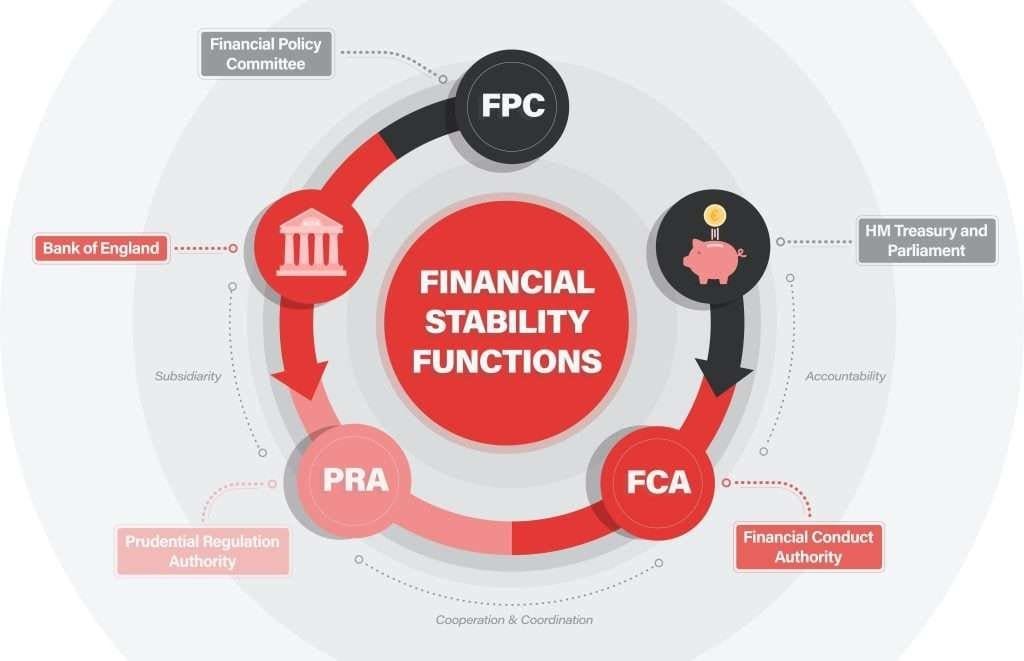
Professional Clients
Professional clients, on the other hand, are deemed to have sufficient experience, knowledge, and financial strength to make their own investment decisions and accurately assess the risks involved. Being classified as a professional client offers several advantages, such as access to a wider range of products and higher leverage options, which can amplify both gains and losses. However, this status comes with reduced regulatory protections. Professional clients forfeit the right to FSCS compensation and access to the Financial Ombudsman Service. They are also subject to less stringent communication rules, under the assumption that they are more capable of understanding complex financial information and the associated risks.
Qualifying as a Professional Client

To be classified as a professional client for CFD trading and spread betting, individuals or entities must meet at least two of the following criteria:
- Size of Financial Instrument Portfolio: The size of the client’s financial instrument portfolio, including cash deposits and financial instruments, exceeds €500,000.
- Experience: The client has worked in the financial sector for at least one year in a professional position that requires knowledge of the transactions or services envisaged.
- Frequency of Transactions: The client has carried out transactions, in significant size, on the relevant market at an average frequency of 10 per quarter over the previous four quarters.
Entities such as large companies, national and regional governments, other institutional investors, and clients who meet these criteria can also request to be treated as professional clients, provided they undergo a rigorous assessment by the firm.
It’s important to note that individuals who do not automatically qualify as professional clients based on the above criteria may still opt for this classification by passing an “appropriateness test” or “elective professional” assessment conducted by the firm offering the financial products. This process involves an evaluation of the individual’s expertise, experience, and knowledge to ensure they are capable of making their own investment decisions and understanding the risks involved.
To become an elective professional client, individuals must:
- Request Reclassification: The client must request a change in classification from the firm with which they are trading.
- Qualify Through Assessment: They must demonstrate their market knowledge, experience, and financial capacity to bear the risks of trading at a professional level.
- Provide Declarations: The client and the firm must mutually agree on the change in classification, with the client acknowledging the loss of protections that accompany retail status.
The Rules Governing Professional Clients

Professional clients operate under a different set of rules compared to retail clients, primarily due to their presumed level of knowledge and experience. Some of these rules include:
- Risk Warnings: Firms may not be required to provide professional clients with the same standard of risk warnings that are mandatory when dealing with retail clients.
- Leverage Limits: Professional clients have access to higher leverage limits compared to retail clients. For CFD trading and spread betting, retail clients face restrictions on leverage that significantly reduce the amount of borrowed funds they can use for trading. Professional clients, however, can negotiate higher leverage based on their agreement with the firm.
- Negative Balance Protection: Retail clients are afforded negative balance protection by the FCA, ensuring they cannot lose more money than they have in their trading account. Professional clients might not automatically receive this protection and may be subject to additional risks.
- Financial Ombudsman Service (FOS): Professional clients may not have access to the FOS or the Financial Services Compensation Scheme (FSCS) in the same way that retail clients do.
What Professional Clients Can Trade vs. Retail Clients
The main difference between what professional and retail clients can trade lies in the restrictions placed on the latter. Retail clients are subject to leverage caps, which can limit the range and size of the positions they can take. For instance, leverage for major currency pairs is capped at 30:1 for retail clients, while professional clients can access higher leverage, potentially increasing their exposure to both gains and losses.
Moreover, some complex and inherently riskier financial instruments might only be available to professional clients, given their supposed ability to understand and manage the associated risks. In the UK, for instance, this means the professional can trade cryptocurrencies, retail traders cannot.
Becoming a Professional Client
The process of becoming a professional client typically involves the following steps:
- Self-Assessment: The client must first assess whether they meet the criteria mentioned above.
- Application: The client must formally apply to their broker or financial institution to be classified as a professional client. This usually involves filling out a questionnaire detailing their trading experience, financial assets, and knowledge of the financial markets.
- Evidence: The client must provide evidence to support their application. This could include documentation of their financial assets, proof of professional experience in the financial sector, or records of their trading history.
- Assessment by the Firm: The broker or financial institution will assess the application against the regulatory criteria to determine if the client can be classified as a professional.
- Risk Acknowledgement: The client must acknowledge in writing that they are aware of the protections they lose by becoming a professional client.
Conclusion
The classification of clients into professional and retail categories is a regulatory measure designed to ensure that investors are provided with a level of protection commensurate with their understanding and experience of financial markets. While the professional client status allows for greater flexibility and access to advanced trading tools and products, it comes with reduced protections and higher risks.
Individuals and entities considering this status must thoroughly assess their ability to manage these risks. Becoming a professional client involves a rigorous application process, including a self-assessment of one’s experience, knowledge, and financial situation, followed by a formal assessment by the financial institution. As the financial landscape continues to evolve, both professional and retail traders must stay informed about the regulations and protections that apply to their trading activities.
James is a former FTSE100 AI Director and trader with 10+ years trading his own capital. He is the Managing Director of SpreadBet.AI and currently trades his own capital through both CFD trading & spread betting as well as working with one of the leading prop firms in the world.

![The Best Forex Spread Betting Broker in the UK [2025]](https://spreadbet.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/joshua-mayo-bmj1Vl77ZWM-unsplash-450x338.jpg)


![The Best Forex Spread Betting Broker in the UK [2025]](https://spreadbet.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/joshua-mayo-bmj1Vl77ZWM-unsplash-100x100.jpg)









