Spread betting has become a popular way for traders to speculate on the movement of financial markets without owning the underlying assets. It offers opportunities to profit from both rising and falling markets. However, spread betting is quite different from traditional forms of trading, and it’s important to understand the specifics before diving in.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll cover what spread betting is, how it works, its advantages and risks, tax implications, and other key aspects. By the end, you should have a thorough understanding of whether spread betting is the right strategy for you.
What is Spread Betting?
Spread betting is a type of financial speculation where traders bet on whether the price of an asset (like a stock, currency, index, or commodity) will rise or fall. Unlike traditional trading, where you buy and sell actual shares or commodities, spread betting involves betting per point of movement in the asset’s price.
What is Spread Betting?
Spread betting allows you to place a “bet” on the price movement of financial assets without owning them. You are simply betting on whether you believe the price will go up or down. Each “point” of price movement can earn or lose you money based on your stake.
Spread betting is typically conducted via specialized brokers, and it’s available on various markets such as stocks, forex, indices, commodities, and even cryptocurrencies.
Example:
If you believe the price of the FTSE 100 will rise, you place a “buy” bet. If the market moves in your favor, you make a profit. If it moves against you, you incur a loss. Conversely, if you believe the FTSE 100 will fall, you place a “sell” bet and profit from the drop.
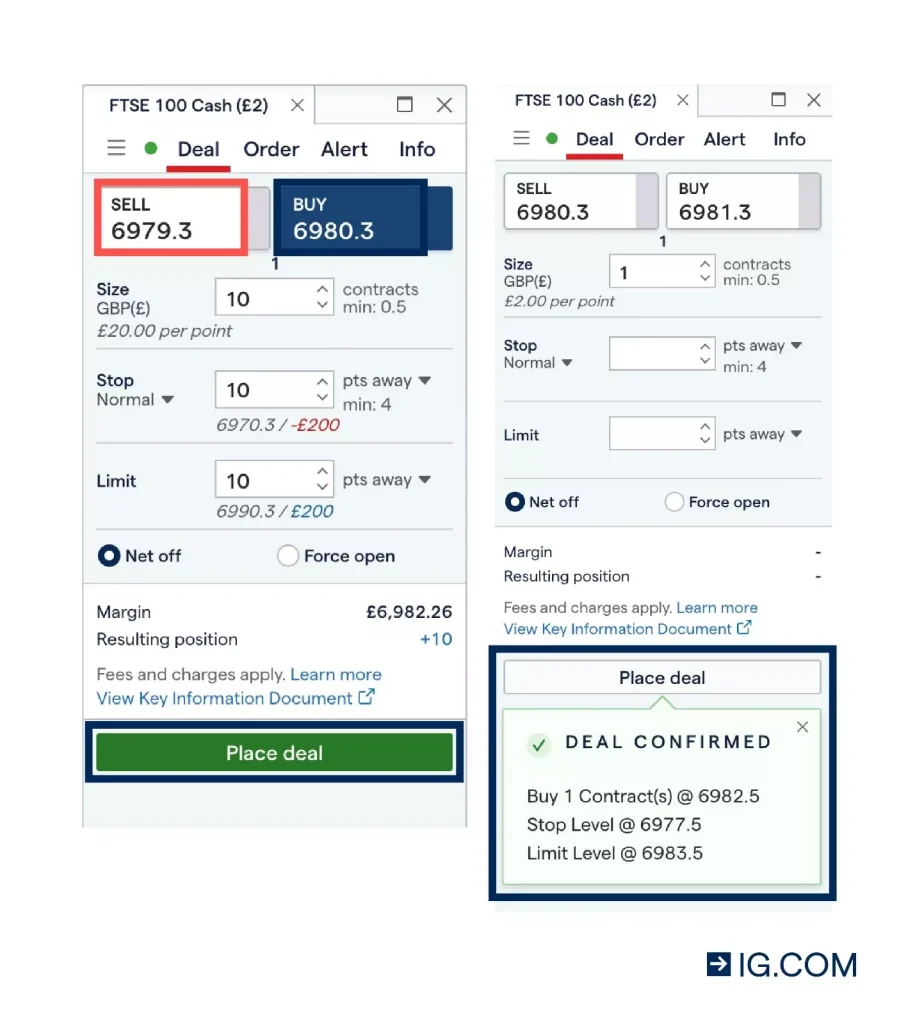
How Does Spread Betting Work?
Spread betting is based on the spread, which is the difference between the buy price (the offer) and the sell price (the bid) set by the broker. Your profit or loss depends on the direction in which you bet (up or down) and how far the market moves in that direction.
What Does It Mean When I Bet Per Point?
When you spread bet, you bet a certain amount of money per point of movement in the market. For example, if you bet £10 per point on the FTSE 100, and the market moves 20 points in your favor, you earn £200 (20 points x £10). If the market moves against you by 20 points, you lose £200.
Advantages of Spread Betting

1. Profit from Rising and Falling Markets
One of the major advantages of spread betting is the ability to profit from both rising and falling markets. You can place a “buy” bet if you think the market will rise or a “sell” bet if you expect it to fall. This makes spread betting more flexible compared to traditional investing, where profits can typically only be made in rising markets.
2. Leverage
Spread betting is a leveraged product, meaning you can control a large position with a smaller initial deposit (known as margin). For example, a £1,000 position may only require a deposit of £100, depending on the leverage offered by the broker. This can amplify profits but also magnify losses.
3. Tax Benefits
Spread betting is tax-free in the UK and some other regions. This means that profits made through spread betting are not subject to capital gains tax or stamp duty.
Is Spread Betting Taxed?
No, spread betting is tax-free in the UK. Since it is classified as betting rather than investing, profits are not subject to capital gains tax or stamp duty. However, this tax-free status may change if HMRC considers your spread betting activity to be a professional trade.
4. No Commissions
Most spread betting brokers do not charge a commission on trades. Instead, the cost is embedded in the spread between the buy and sell prices. This makes it more cost-effective compared to traditional trading, where you may have to pay a broker commission.
Risks of Spread Betting

1. Leverage Risk
While leverage can increase profits, it also increases the risk of losses. Since you’re only required to deposit a small amount of the overall trade size, you can lose more than your initial deposit. For example, if the market moves dramatically against your position, your losses can exceed your margin.
2. Volatility
Spread betting markets, especially those with high leverage, can be volatile. Prices can change rapidly, leading to significant gains or losses in a short amount of time. It’s important to manage risk effectively by using tools such as stop-loss orders to minimize potential losses.
What is a Stop-Loss?
A stop-loss is a risk management tool that automatically closes your position when the market reaches a certain level. This helps to limit your losses by exiting the trade if it moves significantly against you.
3. Market Gaps
Market gaps occur when the price of an asset jumps from one level to another, skipping intermediate prices. If a market opens significantly higher or lower than its previous close (due to overnight news, for example), your stop-loss order may not protect you from large losses.
How to Get Started with Spread Betting
1. Choose a Spread Betting Broker
The first step in spread betting is choosing a regulated broker. Ensure that the broker offers access to the markets you want to trade (e.g., stocks, forex, commodities) and provides a user-friendly platform with risk management tools.
2. Open a Spread Betting Account
Opening an account with a spread betting broker usually involves a simple online application. Many brokers offer demo accounts that allow you to practice without risking real money. This is a great way to get familiar with the platform and learn the basics of spread betting.
3. Place a Trade
Once you have chosen a market to trade, decide whether you expect the price to rise or fall. If you think the price will rise, place a buy bet. If you think it will fall, place a sell bet. Decide how much you want to bet per point of movement, and manage your risk with stop-loss and take-profit orders.
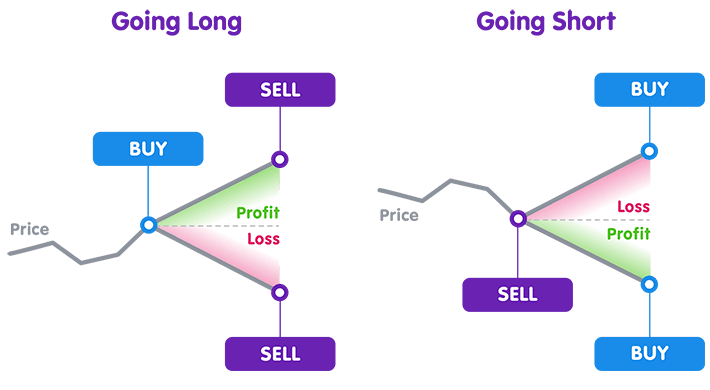
What Does It Mean to Go Long or Short?
When you go long, you are betting that the price of an asset will rise. When you go short, you are betting that the price will fall. Spread betting allows you to profit from either scenario.
Common Spread Betting Terms Explained

1. Margin: The amount of money required to open and maintain a leveraged position. It is a fraction of the total trade size, and it acts as a “good faith” deposit.
2. Spread: The difference between the buy price and the sell price of a market. The broker charges the spread, and it can vary depending on market conditions.
3. Leverage: Allows traders to control larger positions with a smaller deposit, magnifying both potential gains and losses.
4. Points: In spread betting, points refer to the unit of movement in the price of the asset. For example, if the FTSE 100 moves from 7,500 to 7,510, that’s a 10-point movement.
Spread Betting vs. CFD Trading
Spread betting and CFD (Contracts for Difference) trading are similar in that they both allow traders to speculate on the movement of financial markets without owning the underlying asset. However, there are key differences:
- Spread betting is tax-free in the UK, while CFD trading may be subject to capital gains tax.
- CFD trading typically charges commissions, whereas spread betting is usually commission-free.
- CFDs offer more control over leverage levels, and there are often fewer restrictions for professional traders.
What’s the Difference Between Spread Betting and CFD Trading?
While both spread betting and CFDs let you trade on the price movement of assets, spread betting is often preferred in the UK because of its tax-free status. CFD trading, however, is available globally and offers more customization for leverage and other trading conditions.
Is Spread Betting Right for You?
Spread betting can be a powerful tool for profiting from financial markets without the need to own the assets you’re speculating on. Its tax-free status and leveraged trading opportunities make it appealing to many traders. However, it comes with increased risks, especially for inexperienced traders.
Final Considerations:
- Start with a demo account to gain confidence without risking your capital.
- Use risk management tools like stop-loss orders.
- Understand the markets you are betting on and be aware of the risks of leveraged trading.
Conclusion
Spread betting is a versatile way to speculate on financial markets, offering the flexibility to profit from both rising and falling prices. With the right risk management techniques, it can be a rewarding strategy. However, it’s essential to understand the risks involved, particularly when using leverage. Always ensure that you’re trading with a regulated broker and have a solid understanding of how spread betting works before diving into the markets.
Sources:
- https://www.investopedia.com/terms/s/spread-betting.asp
- https://www.daytrading.com/spread-betting
- https://www.ig.com
James is a former FTSE100 AI Director and trader with 10+ years trading his own capital. He is the Managing Director of SpreadBet.AI and currently trades his own capital through both CFD trading & spread betting as well as working with one of the leading prop firms in the world.

![The Best Forex Spread Betting Broker in the UK [2025]](https://spreadbet.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/joshua-mayo-bmj1Vl77ZWM-unsplash-450x338.jpg)


![The Best Forex Spread Betting Broker in the UK [2025]](https://spreadbet.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/joshua-mayo-bmj1Vl77ZWM-unsplash-100x100.jpg)









